Publications
2024
-
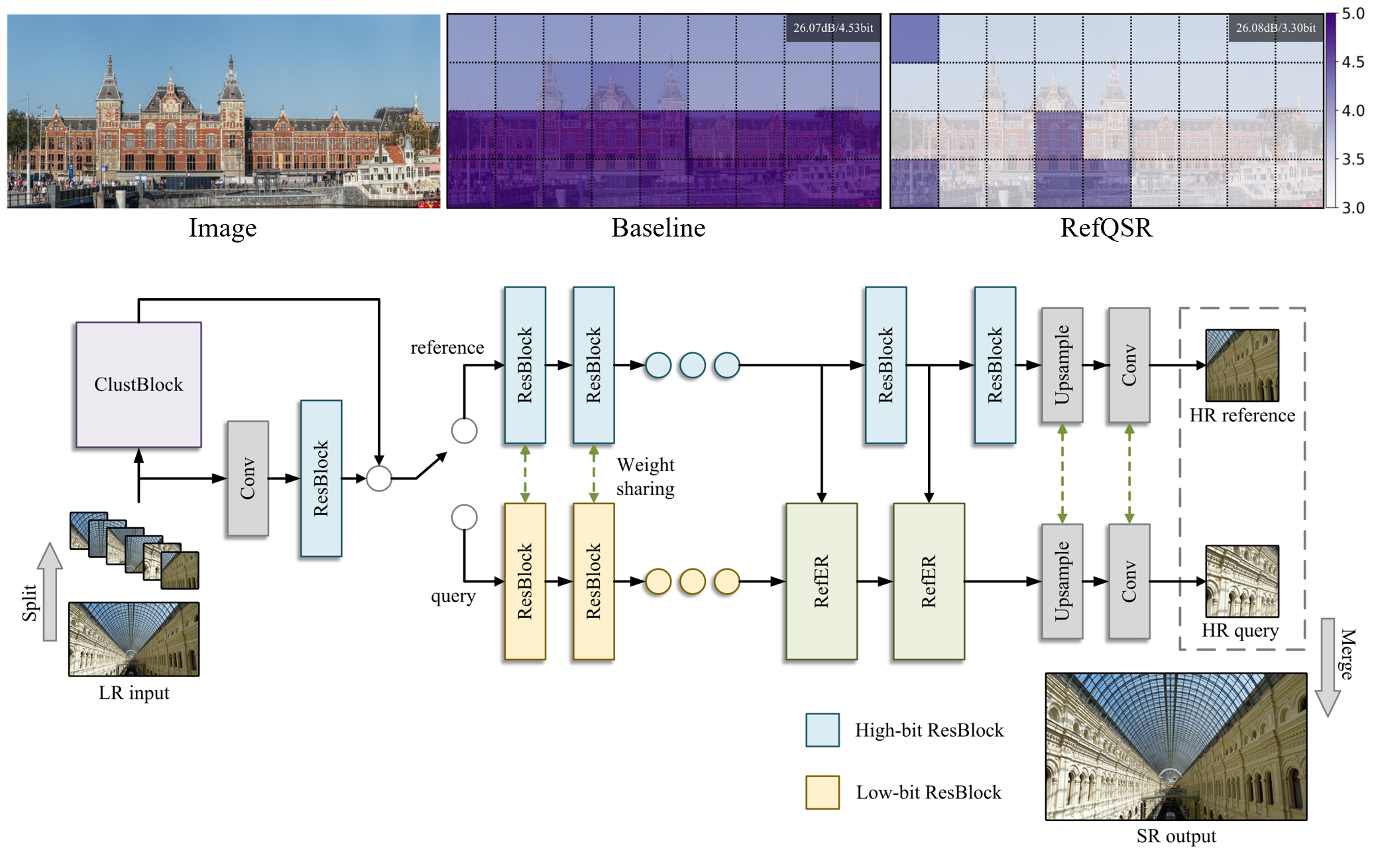 RefQSR: Reference-based Quantization for Image Super-Resolution NetworksLee, Hongjae, Yoo, Jun-Sang, and Jung, Seung-WonIEEE TIP 2024
RefQSR: Reference-based Quantization for Image Super-Resolution NetworksLee, Hongjae, Yoo, Jun-Sang, and Jung, Seung-WonIEEE TIP 2024Single image super-resolution (SISR) aims to reconstruct a high-resolution image from its low-resolution observation. Recent deep learning-based SISR models show high performance at the expense of increased computational costs, limiting their use in resource-constrained environments. As a promising solution for computationally efficient network design, network quantization has been extensively studied. However, existing quantization methods developed for SISR have yet to effectively exploit image self-similarity, which is a new direction for exploration in this study. We introduce a novel method called reference-based quantization for image super-resolution (RefQSR) that applies high-bit quantization to several representative patches and uses them as references for low-bit quantization of the rest of the patches in an image. To this end, we design dedicated patch clustering and reference-based quantization modules and integrate them into existing SISR network quantization methods. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of RefQSR on various SISR networks and quantization methods.
2023
-
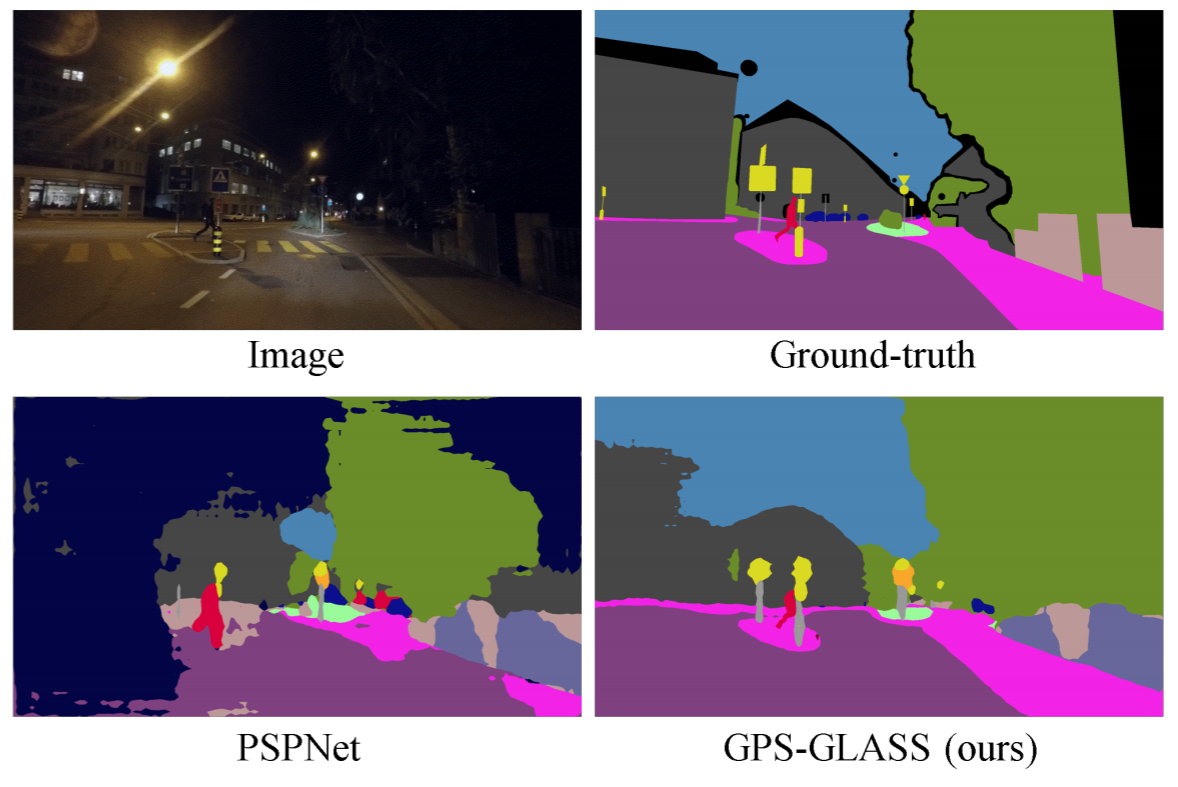 GPS-GLASS: Learning Nighttime Semantic Segmentation Using Daytime Video and GPS dataLee, Hongjae, Han, Changwoo, Yoo, Jun-Sang, and Jung, Seung-WonICCVW (oral) 2023
GPS-GLASS: Learning Nighttime Semantic Segmentation Using Daytime Video and GPS dataLee, Hongjae, Han, Changwoo, Yoo, Jun-Sang, and Jung, Seung-WonICCVW (oral) 2023Semantic segmentation for autonomous driving should be robust against various in-the-wild environments. Nighttime semantic segmentation is especially challenging due to a lack of annotated nighttime images and a large domain gap from daytime images with sufficient annotation. In this paper, we propose a novel GPS-based training framework for nighttime semantic segmentation. Given GPS-aligned pairs of daytime and nighttime images, we perform cross-domain correspondence matching to obtain pixel-level pseudo supervision. Moreover, we conduct flow estimation between daytime video frames and apply GPS-based scaling to acquire another pixel-level pseudo supervision. Using these pseudo supervisions with a confidence map, we train a nighttime semantic segmentation network without any annotation from nighttime images. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on several nighttime semantic segmentation datasets.
-
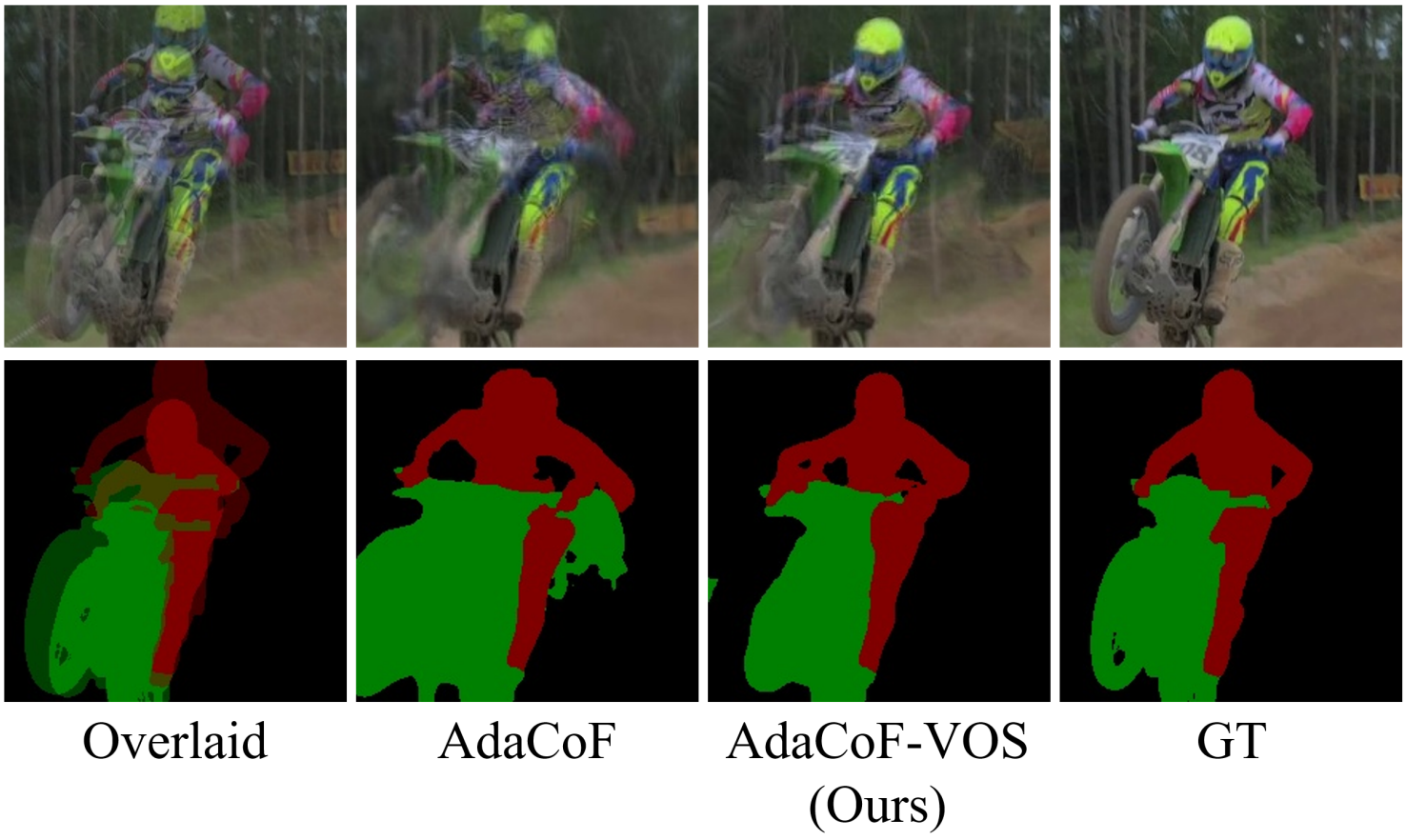 Video Object Segmentation-aware Video Frame InterpolationYoo, Jun-Sang, Lee, Hongjae, and Jung, Seung-WonICCV 2023
Video Object Segmentation-aware Video Frame InterpolationYoo, Jun-Sang, Lee, Hongjae, and Jung, Seung-WonICCV 2023Video frame interpolation (VFI) is a very active research topic due to its broad applicability to many applications, including video enhancement, video encoding, and slow-motion effects. VFI methods have been advanced by improving the overall image quality for challenging sequences containing occlusions, large motion, and dynamic texture. This mainstream research direction neglects that foreground and background regions have different importance in perceptual image quality. Moreover, accurate synthesis of moving objects can be of utmost importance in computer vision applications. In this paper, we propose a video object segmentation (VOS)-aware training framework called VOS-VFI that allows VFI models to interpolate frames with more precise object boundaries. Specifically, we exploit VOS as an auxiliary task to help train VFI models by providing additional loss functions, including segmentation loss and bi-directional consistency loss. From extensive experiments, we demonstrate that VOS-VFI can boost the performance of existing VFI models by rendering clear object boundaries. Moreover, VOS-VFI displays its effectiveness on multiple benchmarks for different applications, including video object segmentation, object pose estimation, and visual tracking.
-
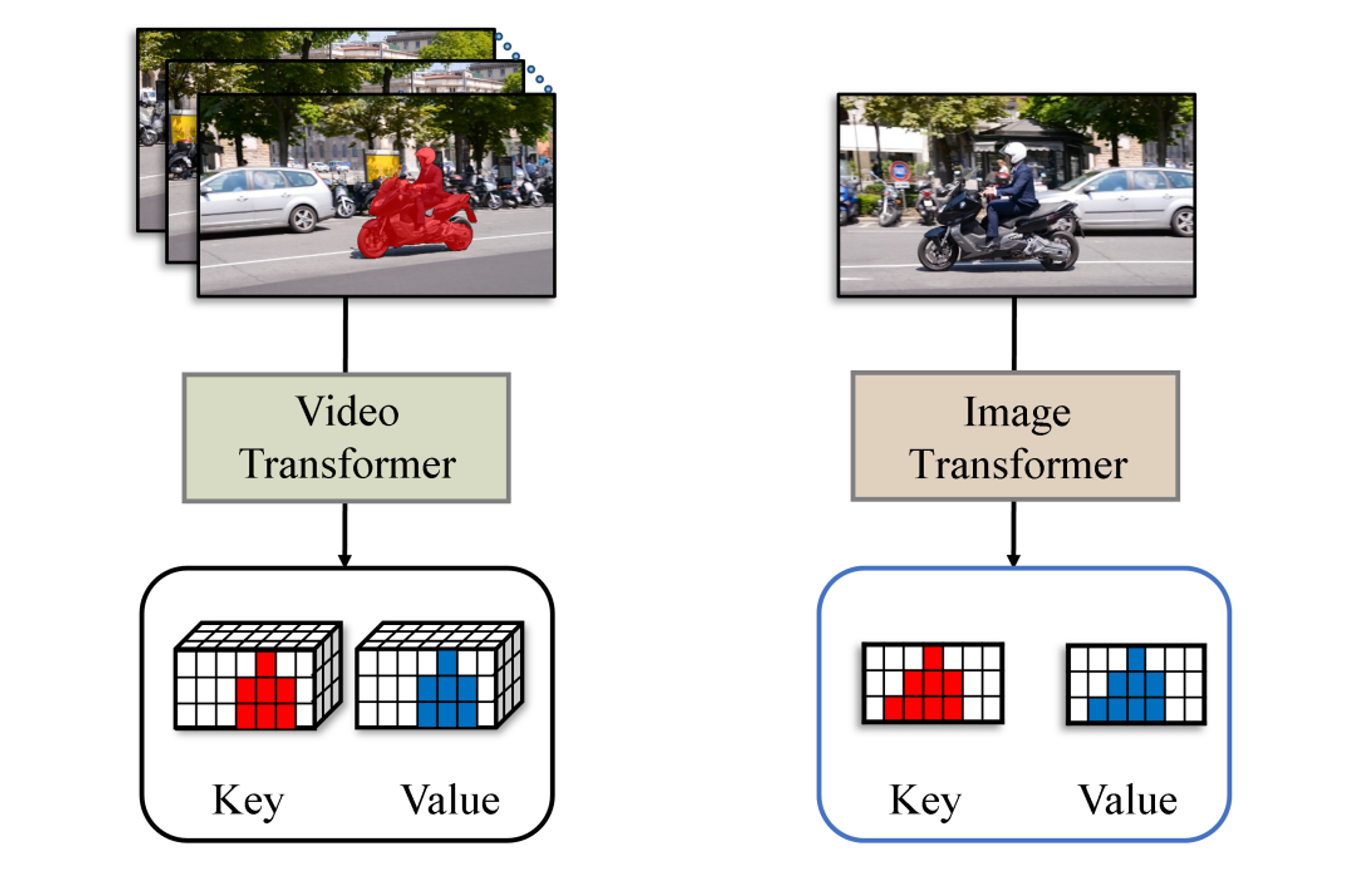 Hierarchical Spatiotemporal Transformers for Video Object SegmentationYoo, Jun-Sang, Lee, Hongjae, and Jung, Seung-WonICCVW (oral) 2023
Hierarchical Spatiotemporal Transformers for Video Object SegmentationYoo, Jun-Sang, Lee, Hongjae, and Jung, Seung-WonICCVW (oral) 2023This paper presents a novel framework called HST for semi-supervised video object segmentation (VOS). HST extracts image and video features using the latest Swin Transformer and Video Swin Transformer to inherit their inductive bias for the spatiotemporal locality, which is essential for temporally coherent VOS. To take full advantage of the image and video features, HST casts image and video features as a query and memory, respectively. By applying efficient memory read operations at multiple scales, HST produces hierarchical features for the precise reconstruction of object masks. HST shows effectiveness and robustness in handling challenging scenarios with occluded and fast-moving objects under cluttered backgrounds. In particular, HST-B outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors on multiple popular benchmarks.
2022
-
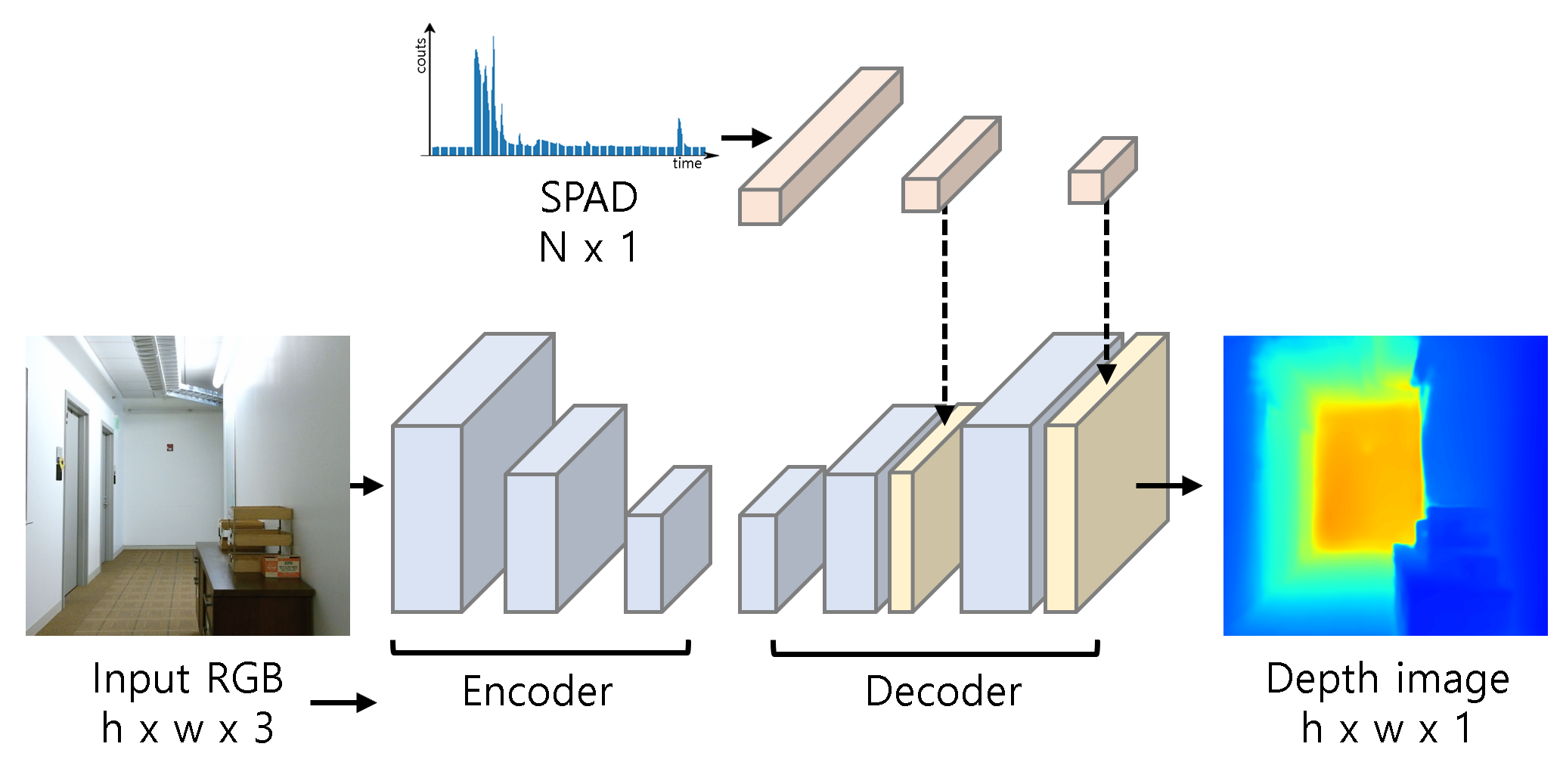 Monocular Depth Estimation Network with Single-Pixel Depth GuidanceLee, Hongjae, Park, Jinbum, Jeong, Wooseok, and Jung, Seung-WonOptics Letters 2022
Monocular Depth Estimation Network with Single-Pixel Depth GuidanceLee, Hongjae, Park, Jinbum, Jeong, Wooseok, and Jung, Seung-WonOptics Letters 2022Due to the scale ambiguity problem, the performance of monocular depth estimation (MDE) is inherently restricted. Multi-camera systems, especially those equipped with active depth cameras, have addressed this problem at the expense of increased hardware costs and space. In this Letter, we adopt a similar but costeffective solution using only single-pixel depth guidance with a single-photon avalanche diode. To this end, we design a single-pixel guidance module (SPGM) that combines the global information from the single-pixel depth guidance with the spatial information from the image at the feature level. By integrating SPGMs into an MDE network, we introduce PhoMoNet, the first end-to-end MDE network with single-pixel depth guidance. Experimental results show the effectiveness and superiority of PhoMoNet over state-of-the-art MDE networks on synthetic and real-world datasets.
2021
-
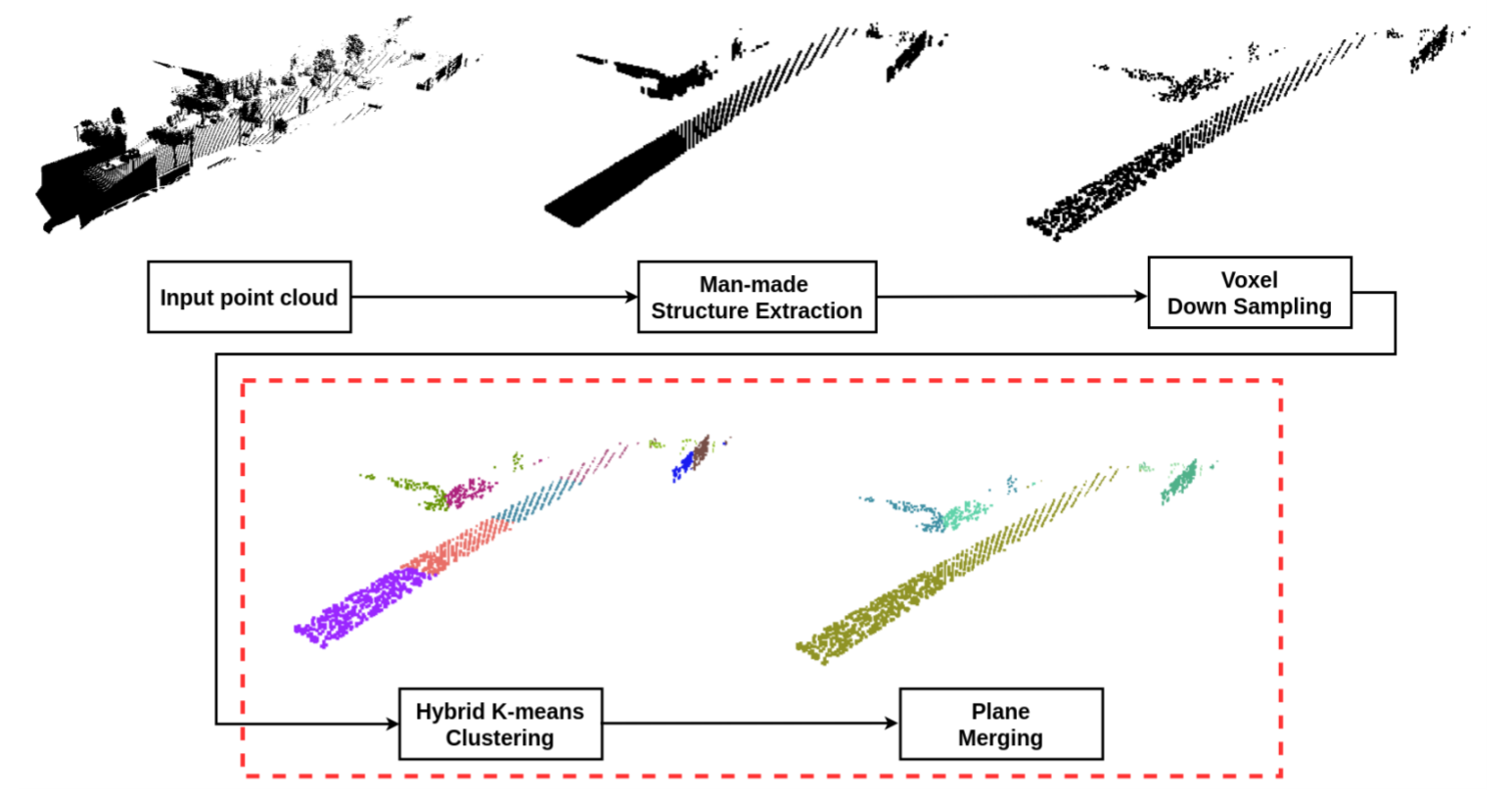 Clustering-based plane segmentation neural network for urban scene modelingLee, Hongjae, and Jung, JiyoungSensors 2021
Clustering-based plane segmentation neural network for urban scene modelingLee, Hongjae, and Jung, JiyoungSensors 2021Urban scene modeling is a challenging but essential task for various applications, such as 3D map generation, city digitization, and AR/VR/metaverse applications. To model man-made structures, such as roads and buildings, which are the major components in general urban scenes, we present a clustering-based plane segmentation neural network using 3D point clouds, called hybrid K-means plane segmentation (HKPS). The proposed method segments unorganized 3D point clouds into planes by training the neural network to estimate the appropriate number of planes in the point cloud based on hybrid K-means clustering. We consider both the Euclidean distance and cosine distance to cluster nearby points in the same direction for better plane segmentation results. Our network does not require any labeled information for training. We evaluated the proposed method using the Virtual KITTI dataset and showed that our method outperforms conventional methods in plane segmentation. Our code is publicly available.